Understanding CKD Treatment Options for Kidney Health Awareness
Introduction: The Significance of CKD Treatment
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive condition that affects millions worldwide, impairing kidney function over time. Early detection and effective treatment are crucial to managing the disease and maintaining quality of life. Understanding CKD treatment options is vital for patients and caregivers, as it enables informed decision-making and proactive health management. This article explores various aspects of CKD treatment, offering insights into the approaches that can help manage this complex condition.
Conservative Management: A Non-Invasive Approach
Conservative management is often the first line of defense in treating CKD, particularly in its early stages. This approach focuses on lifestyle modifications and medication to slow disease progression and manage symptoms. Key components include:
- Dietary Changes: Reducing sodium, potassium, and phosphorus intake can help manage CKD symptoms and prevent further kidney damage.
- Blood Pressure Control: Medications such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs can help maintain optimal blood pressure levels, reducing stress on the kidneys.
- Blood Sugar Management: For patients with diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent kidney damage.
Conservative management emphasizes patient education and regular monitoring to ensure adherence to treatment plans. By making informed lifestyle choices, individuals with CKD can significantly impact their disease progression and overall health.
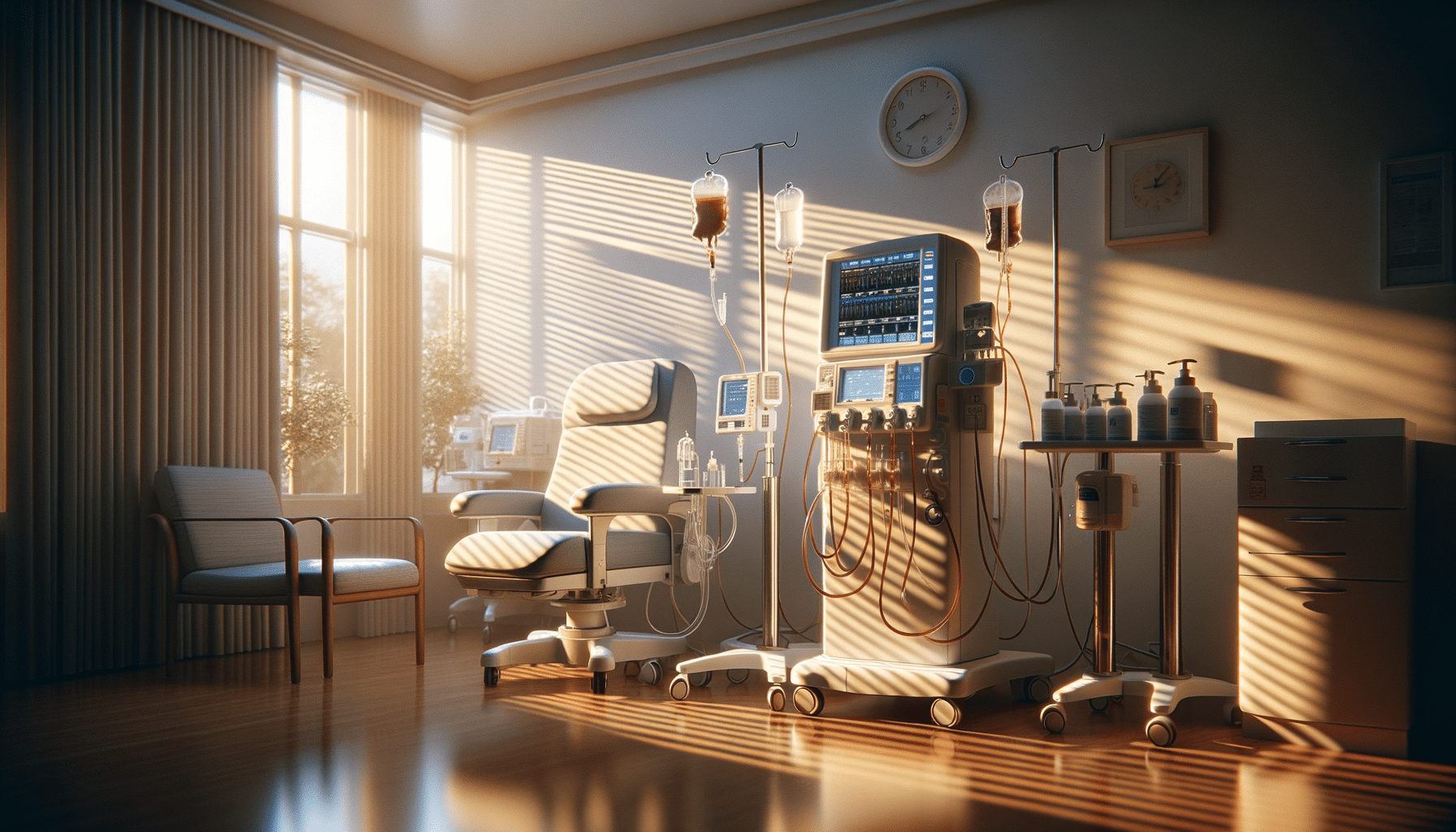
Dialysis: An Essential Lifeline for Advanced CKD
For patients with advanced CKD, dialysis becomes a critical component of treatment. This medical intervention performs the essential function of filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, a task the kidneys can no longer manage. There are two primary types of dialysis:
- Hemodialysis: This process involves using a machine to clean the blood, typically performed at a dialysis center several times a week.
- Peritoneal Dialysis: This method involves using the lining of the abdomen to filter blood, allowing treatment to be conducted at home.
Dialysis can significantly improve the quality of life for CKD patients by managing symptoms and preventing complications. However, it requires a significant time commitment and lifestyle adjustments, underscoring the importance of a supportive care network.
Kidney Transplant: A Long-Term Solution
A kidney transplant offers a long-term solution for CKD patients, providing a new, functioning kidney to replace the failing ones. This option is generally considered for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The benefits of a kidney transplant include:
- Improved Quality of Life: Transplant recipients often experience better health outcomes and greater freedom in daily activities compared to those on dialysis.
- Increased Longevity: Studies suggest that kidney transplants can extend life expectancy compared to long-term dialysis.
However, a kidney transplant requires lifelong immunosuppressive medication to prevent rejection, and there are risks associated with the surgery and medication. Despite these challenges, many patients find that the benefits of a transplant outweigh the risks, making it a viable option for long-term CKD management.
Conclusion: Navigating CKD Treatment Options
Treating CKD involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual needs of each patient. From conservative management to dialysis and kidney transplants, understanding the available options empowers patients and caregivers to make informed decisions. The journey through CKD treatment is unique for everyone, but with the right resources and support, patients can navigate their path to better kidney health with confidence.